Optimal placement and sizing of distributed generation units in distribution networks using an enhanced particle swarm optimization framework
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2026.1.02Keywords:
distributed generation, particle swarm optimization, Dehghani method, voltage deviation, power loss minimization, distribution networksAbstract
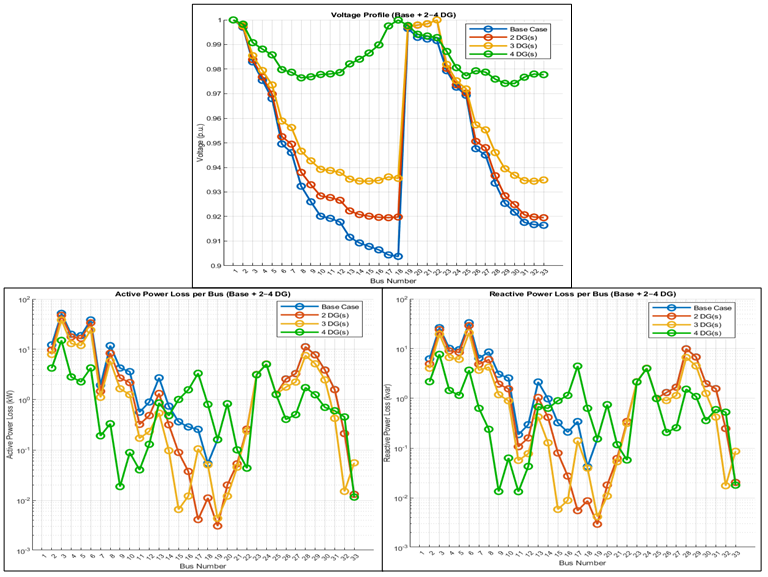
Introduction. Optimal planning of distributed generation (DG) units is a critical research topic due to the growing integration of renewable energy and the need to enhance distribution network performance. Classical optimization methods often struggle with the nonlinear, nonconvex, and highly coupled nature of DG allocation problems. Problem. The IEEE 33-bus distribution network experiences significant voltage drops and high active and reactive power losses under normal operating conditions. Determining the optimal placement and sizing of DG units is a complex problem involving multiple interacting variables and operational constraints. Goal. This study aims to improve technical performance by minimizing total active power losses and voltage deviation while ensuring voltage stability and network reliability. Methodology. The particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is enhanced using the Dehghani method (DM) – a population-based modification framework allowing all individuals, including the worst member, to contribute in improving the best solution. The improved PSO-DM algorithm is applied to the IEEE 33 bus system under four cases: the base case without DG and scenarios with 2, 3 and 4 DG units. The objective function includes active power loss minimization and total voltage deviation. Results. The 4-DG configuration significantly improves system performance: active power losses decrease from 210.67 kW to 53.9 kW (74.4 % reduction), reactive losses drop from 142.84 kVAr to 38.42 kVAr (73.1 % reduction), the minimum bus voltage rises from 0.9037 to 0.9741 p.u. and total voltage deviation decreases from 1.8037 p.u. to 0.5129 p.u. (71.6 % improvement). These results demonstrate that PSO-DM effectively balances exploration and exploitation, yielding superior DG allocation solutions. Scientific novelty. Integrating DM into PSO introduces a cooperative solution-refinement mechanism that enhances convergence speed and search accuracy. Practical value. The PSO-DM framework provides a reliable and computationally efficient tool for DG planning in modern smart distribution networks. References 22, tables 1, figures 3.
References
Cavus M. Advancing Power Systems with Renewable Energy and Intelligent Technologies: A Comprehensive Review on Grid Transformation and Integration. Electronics, 2025, vol. 14, no. 6, art. no. 1159. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061159.
Malika B.K., Pattanaik V., Sahu B.K., Rout P.K., Panda S., Bajaj M. Optimal distributed generation and shunt capacitor bank placement in microgrid distribution planning for enhanced performance. Neural Computing and Applications, 2025, vol. 37, no. 22, pp. 17363-17388. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10503-9.
Georgilakis P.S., Hatziargyriou N.D. Optimal Distributed Generation Placement in Power Distribution Networks: Models, Methods, and Future Research. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 3420-3428. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2012.2237043.
Mazurenko L.I., Dzhura O.V., Shykhnenko M.O. Steady-state analysis of a hybrid power supply system using an induction generator with a shunt AC/DC converter. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2024, no. 2, pp. 67-74. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2024.2.10.
Tami Y., Sebaa K., Lahdeb M., Usta O., Nouri H. Extended mixed integer quadratic programming for simultaneous distributed generation location and network reconfiguration. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 2, pp. 93-100. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.2.14.
Manohara M., Veera Reddy V.C., Vijaya Kumar M. Exploration and mitigation of power quality problems in radial distribution system by placing distributed generation through voltage stability index. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 2, pp. 79-85. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.2.12.
Pepermans G., Driesen J., Haeseldonckx D., Belmans R., D’haeseleer W. Distributed generation: definition, benefits and issues. Energy Policy, 2005, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 787-798. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2003.10.004.
Sabry S.S., Al-Yozbaky O.S. Enhanced siting and sizing of distributed generation in radial distribution networks under load demand uncertainty using a hybrid metaheuristic framework. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2025, no. 6, pp. 84-92. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.6.11.
Neda O.M. Optimal amalgamation of DG units in radial distribution system for techno-economic study by improved SSA: Practical case study. Electric Power Systems Research, 2025, vol. 241, art. no. 111365. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2024.111365.
Rajakumar P., Balasubramaniam P.M., Parimalasundar E., Suresh K., Aravind P. Optimized placement and sizing of solar photovoltaic distributed generation using jellyfish search algorithm for enhanced power system performance. Scientific Reports, 2025, vol. 15, no. 1, art. no. 20755. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-08227-4.
Rajakumar P., Balasubramaniam P.M., Aldulaimi M.H., Arunkumar M., Ramesh S., Alam M.M., Al-Mdallal Q.M. An integrated approach using active power loss sensitivity index and modified ant lion optimization algorithm for DG placement in radial power distribution network. Scientific Reports, 2025, vol. 15, no. 1, art. no. 10481. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-87774-2.
Bouchikhi N., Boussadia F., Bouddou R., Salau A.O., Mekhilef S., Gouder C., Adiche S., Belabbes A. Optimal distributed generation placement and sizing using modified grey wolf optimization and ETAP for power system performance enhancement and protection adaptation. Scientific Reports, 2025, vol. 15, no. 1, art. no. 13919. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-98012-0.
Prasad K.R.K.V., Kollu R., Ramkumar A., Ramesh A. A multi-objective strategy for optimal DG and capacitors placement to improve technical, economic, and environmental benefits. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2025, vol. 165, art. no. 110491. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2025.110491.
Alhasnawi B.N., Zanker M., Bureš V. A new smart charging electric vehicle and optimal DG placement in active distribution networks with optimal operation of batteries. Results in Engineering, 2025, vol. 25, art. no. 104521. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2025.104521.
Sahay S., Biswal S.R., Shankar G., Jha A.V., Appasani B., Srinivasulu A., Nsengiyumva P. Optimized placement of distributed generators, capacitors, and EV charging stations in reconfigured radial distribution networks using enhanced artificial hummingbird algorithm. Scientific Reports, 2025, vol. 15, no. 1, art. no. 11144. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-89089-8.
Islam A., Rudra S., Kolhe M.L. Optimizing the placement of distributed energy storage and improving distribution power system reliability via genetic algorithms and strategic load curtailment. Neural Computing and Applications, 2025, vol. 37, no. 22, pp. 17589-17608. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-025-11037-4.
Qawaqneh H., Alomari K.M., Alomari S., Bektemyssova G., Smerat A., Montazeri Z., Dehghani M., Malik O.P., Eguchi K. Black-breasted Lapwing Algorithm (BBLA): A Novel Nature-inspired Metaheuristic for Solving Constrained Engineering Optimization. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems, 2025, vol. 18, no. 11, pp. 581-597. doi: https://doi.org/10.22266/ijies2025.1231.36.
Qawaqneh H., Alomari K.M., Alomari S., Bektemyssova G., Smerat A., Montazeri Z., Dehghani M., Malik O.P., Eguchi K. Kakapo Optimization Algorithm (KOA): A Novel Bio-inspired Metaheuristic for Optimization Applications. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems, 2025, vol. 18, no. 11, pp. 913-929. doi: https://doi.org/10.22266/ijies2025.1231.56.
Zraiqat A., Batiha B., Al-Refai O., Al-Salih A.A.M.M., Smerat A., Montazeri Z., Dehghani M., Werner F., Ahmed M.A., Ibraheem I.K., Eguchi K. Psychologist Algorithm: A Human-inspired Metaheuristic for Solving Complex Constrained Optimization Problems. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems, 2025, vol. 18, no. 9, pp. 124-137. doi: https://doi.org/10.22266/ijies2025.1031.09.
Kennedy J., Eberhart R. Particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of ICNN’95 – International Conference on Neural Networks, 1995, vol. 4, pp. 1942-1948. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968.
Dehghani M., Montazeri Z., Dehghani A., Samet H., Sotelo C., Sotelo D., Ehsanifar A., Malik O.P., Guerrero J.M., Dhiman G., Ramirez-Mendoza R.A. DM: Dehghani Method for Modifying Optimization Algorithms. Applied Sciences, 2020, vol. 10, no. 21, art. no. 7683. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217683.
Baran M.E., Wu F.F. Network reconfiguration in distribution systems for loss reduction and load balancing. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1989, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 1401-1407. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/61.25627.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 M. Al Soudi, O. Alsayyed, B. Batiha, T. Hamadneh, O. P. Malik, M. Dehghani, Z. Montazeri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




