Theory and practice of numerical-field analysis and refinement of electromagnetic and energy parameters in the designs of three-phase induction motors
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2026.1.01Keywords:
three-phase induction motor, automated numerical-field calculations, magnetic field, FEMM, electromagnetic and energy parameters, verification and refinement of design dataAbstract
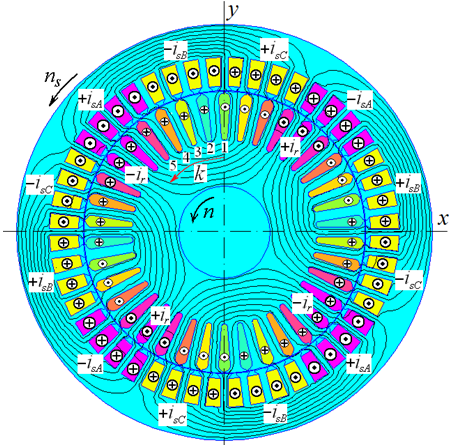
Introduction. The paper is devoted to improving the designs of three-phase induction motors (TIMs) based on the application of numerical calculations of their magnetic fields. Considering that the classical system for designing TIMs does not always provide sufficient accuracy of their design parameters, this task is relevant and therefore the developed motors require experimental refinement and additional time and money accordingly. Problem. In classic design of TIMs, magnetic calculations are performed based on magnetic circuit theory. The magnetic circuit of TIMs is divided into conditionally homogeneous sections, on which the magnetic quantities are considered to be distributed evenly, but their real distribution is much more complicated. This approach leads to error in determining the electromagnetic parameters of TIMs and, as a result, inaccuracies in energy, mechanical, thermal, etc. calculations. The goal of the paper is to further develop the existing system for designing TIMs by refining it using numerical-field calculations of electromagnetic and energy parameters. Methodology. The methodology is based on numerical-field verification and refinement of classical design of TIMs. It is strictly deterministic, despite the complexity of linear and nonlinear interrelationships of its structural, electromagnetic, and energy parameters, and therefore it is amenable to adequate algorithmization and programming using iterative calculations. The theoretical foundations of the methodology are reinforced by harmonic analysis of time functions of electromagnetic quantities and a refined determination of the differential leakage resistance of the stator winding. The tool for implementing the methodology is the FEMM program in conjunction with the created Lua scripts. Results. Numerical-field calculations of the electromagnetic and energy parameters of the test TIM developed according to the classical design were performed. This motor has been tested within the synchronous idle and rated load conditions. This demonstrated a sufficiently high efficiency of the provided theoretical and practical foundations of numerical-field calculations and revealed that the TIM project does not meet the declared power and voltage requirement. To reach their nominal values, the method for refining the magnetizing current of the stator winding and the rotor slip is provided. Scientific novelty of this paper is the system of numerical-field calculations of electromagnetic and energy parameters of TIMs, which, in conjunction with the iterative process, ensures its output to the specified nominal stator winding voltage and output power while simultaneously varying the magnetizing current and slip. Practical value. The methodology of numerical-field calculations of TIMs based on the FEMM program and the Lua script is recommended to be integrated into the automated design system for these motors. In addition to verifying and refining the parameters of the designed TIMs, the developed methodology and program can be used to obtain a set of refined operating characteristics in an automated calculation mode. References 29, tables 5, figures 9.
References
Finite Element Method Magnetics: Download – Stable Distribution (21Apr2019) – 64-bit Executable. Available at: https://www.femm.info/wiki/Download (Accessed 05 May 2025).
Ierusalimschy R. Reference Manual of the Programming Language Lua 4.0. Available at: http://www.lua.org/manual/4.0/ (Accessed 05 May 2025).
Goldberg O.D., Gurin Ya.S., Sviridenko I.S. Design of electrical machines. 2nd ed., revised and additional. Moscow, Higher School Publ., 2001. 430 p. (Rus).
Kopylov I.P. Electrical machines designing. Moscow, Yurait Publ., 2019. 828 p. (Rus).
Milykh V.I. Numerically-field analysis of the adequacy of the design data of three-phase induction motors and the method of their refinement on this basis. Technical Electrodynamics, 2018, no. 1, pp. 47-55. (Rus). doi: https://doi.org/10.15407/techned2018.01.047.
Milykh V.I. Numerical-field analysis of temporal functions and harmonic composition of EMF in windings of a three-phase asynchronous motor. Technical Electrodynamics. 2018, no. 3, pp. 56-65. (Rus). doi: https://doi.org/10.15407/techned2018.03.056.
Milykh V.I. The system of automated formation of electrical machines computational models for the FEMM software environment. Technical Electrodynamics. 2018, no. 4, pp. 74-78. (Ukr). doi: https://doi.org/10.15407/techned2018.04.074.
Milykh V.I. Numerical-field analysis of active and reactive winding parameters and mechanical characteristics of a squirrel-cage induction motor. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 4, pp. 3-13. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.4.01.
Milykh V.I. Numerical-field analysis of differential leakage reactance of stator winding in three-phase induction motors. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2025, no. 2, pp. 7-18. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.2.02.
Göztaş M., Çunkaş M., Şahman M.A. In-Situ Efficiency Estimation of Induction Motors Using Whale Optimization Algorithm. Turkish Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2025, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 114-124. doi: https://doi.org/10.5152/tepes.2025.25001.
Michael I.N., Eneh P.I.I. Optimization of a Single-Phase Induction Motor Using Finite Element Method. International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews, 2025, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 4441-4449. doi: https://doi.org/10.55248/gengpi.6.0225.1020.
Ding Q., Yang Z., Sun X., Zhao Q., Zhu H. Analysis of rotor slot width influence on a bearingless induction motor. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2020, vol. 81, art. no. 106534. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2019.106534.
Arish N., Ardestani M., Hekmati A. Optimum Structure of Rotor Slot for a 20 kW HTS Induction Motor. Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications, 2021, vol. 582, art. no. 1353829. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.2021.1353829.
Ocak C. A FEM-Based Comparative Study of the Effect of Rotor Bar Designs on the Performance of Squirrel Cage Induction Motors. Energies, 2023, vol. 16, no. 16, art. no. 6047. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en16166047.
Nascimento D., Smolenski R., Loschi H., Grassi F., Wan L., Hamid A. Electromagnetic Fields on 3-Phase Induction Motor Using Finite Element Analysis. 2021 IEEE International Joint EMC/SI/PI and EMC Europe Symposium, 2021, pp. 434-439. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EMC/SI/PI/EMCEurope52599.2021.9559357.
Ding Z., Bu W., Cai X., Wu X., Liu S. Finite Element Analysis and Modeling of Three-Phase Induction Motor. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, vol. 677, no. 5, art. no. 052055. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/677/5/052055.
Lee J.-H., Kwon Y.-C., Sul S.-K. High-Fidelity Induction Motor Simulation Model Based on Finite Element Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, vol. 69, no. 10, pp. 9872-9883. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2022.3163556.
Ekpo E.G. Dynamic Analysis of Two Phase Induction Motor Using Finite Element Method. Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS), 2020, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 211-218. Available at: https://www.scholarlinkinstitute.org/jeteas/abstractview.php?id=6.83 (Accessed 05 May 2025).
Shaier A.A., Flah A., Kraiem H., Enany M.A., Elymany M.M. Novel technique for precise derating torque of induction motors using ANFIS. Scientific Reports, 2025, vol. 15, no. 1, art. no. 8550. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-92821-z.
Asaad M., Mejbel A. Losses estimation of a single - phase induction motor based on finite element analysis. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2023, vol. 2787, no. 1, art. no. 050019. doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0148207.
Breivik A. Fault Detection and Diagnosis of Induction Motor for Ship Propulsion by utilizing Electrical Signature and Finite Element Method. Master’s thesis in Marine Technology. NTNU, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2021, 107 p. Available at: https://ntnuopen.ntnu.no/ntnu-xmlui/handle/11250/2781526 (Accessed 05 May 2025).
Babu H. Finite-element analysis of an induction motor with inter-turn short-circuit faults. Thesis of Master in Electrical Engineering. KTH Royal Institute of Technology, School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS), Stockholm, Sweden, 2020, 98 p. Available at: https://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:kth:diva-290082 (Accessed 05 May 2025).
Liang X., Ali M.Z., Zhang H. Induction Motors Fault Diagnosis Using Finite Element Method: A Review. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2020, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 1205-1217. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2019.2958908.
Sakhara S., Brahimi M., Nacib L., Layadi T.M. Application of a wavelet neural network approach to detect stator winding short circuits in asynchronous machines. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 3, pp. 21-27. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.3.03.
Diarra M.N., Li Y., Zhao X. Induction Motors Parameters Identification by Starting Process Using Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization-Trust Region Algorithm (QPSO-TRA). 2023 International Conference on Applied Intelligence and Sustainable Computing (ICAISC), 2023, pp. 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAISC58445.2023.10200090.
Popovych O., Golovan I. Currents System for Efficient Mathematical Modeling of an Induction Motor Using the Field Analysis. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Modern Electrical and Energy Systems (MEES), 2019, pp. 142-145. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MEES.2019.8896624.
Golovan I.V., Popovych O.M. Consideration of the induced current displacement in the rotor circuit in a weakly coupled circuit-field model of an induction motor. Technical Electrodynamics, 2025, no. 3, pp. 22-30. (Ukr). doi: https://doi.org/10.15407/techned2025.03.022.
Quadrado J.C. Enhancing Engineering Education: Integrating Finite Element Method Analysis for Induction Motors Efficiency Improvement Study. Proceedings of the 22nd LACCEI International Multi-Conference for Engineering, Education and Technology: Sustainable Engineering for a Diverse, Equitable, and Inclusive Future at the Service of Education, Research, and Industry for a Society 5.0, 2024, art. no. 2032. doi: https://doi.org/10.18687/LACCEI2024.1.1.2032.
Milykh V.I., Polyakova N.V. Harmonious analysis of electromagnetic sizes three-phase winding of stators of turbogenerator on basis classic and numeral field methods. Technical Electrodynamics, 2013, no. 3, pp. 40-49. (Rus).
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 V. I. Milykh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




