Regulation characteristics of a step-down pulse regulator in continuous and discontinuous conduction mode
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.5.08Keywords:
discontinuous conduction mode, control characteristics of a pulse regulator, ripple coefficient of the output voltageAbstract
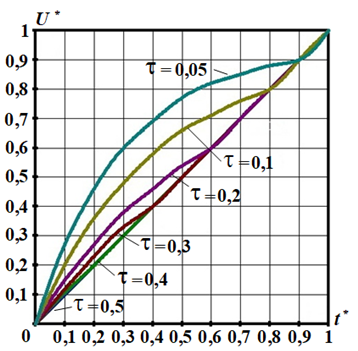
Introduction. Pulse regulators (PRs) are widely used to regulate and stabilize the supply voltage of DC consumers. The main characteristic of any regulator is its regulation characteristic. In the general case, two modes of PR operation are possible: continuous conduction mode and discontinuous conduction mode in the inductance of the PR. Problem. When the PR transitions from one operating mode to another, its regulation characteristics change. In the continuous conduction mode, the regulation characteristic is a function of one variable. In the discontinuous conduction mode, the regulation characteristic becomes a function of two variables. Therefore, in such a mode, PR is described by a family of regulation characteristics. The goal of the work is to develop a mathematical model that describes the operation of the controller in both continuous and discontinuous conduction modes, as well as to determine the control characteristics that are valid for both of these modes. Methodology. In the work, using the example of a step-down type PR, the conditions for the PR transition from one operating mode to another are determined, as well as the dependence of the PR output voltage on the duration of the pause in the inductance current. Results. The influence of the parameters of the PR elements on the pause duration is analyzed. A graph of the family of PR control characteristics is constructed, which is valid for both continuous and discontinuous conduction modes. Scientific novelty. It is shown that when PR transitions to discontinuous conduction mode, its control characteristics shift towards higher output voltages. This shift is greater, the longer the pause duration in the inductance current. Practical value. It is determined that the specified ripple coefficient of the PR output voltage in the discontinuous conduction mode is provided by a smaller value of the LC product of the PR elements, compared to the continuous conduction mode. References 17, tables 2, figures 5.
References
Valarmathy A.S., Prabhakar M. High gain interleaved boost-derived DC-DC converters – A review on structural variations, gain extension mechanisms and applications. E-Prime - Advances in Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Energy, 2024, vol. 8, art. no. 100618. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prime.2024.100618.
Romashko V.Y., Batrak L.M., Abakumova O.O. Features of the work of pulse regulators in the maximum power transmission mode, with the presence of an accumulator at their output. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 6, pp. 63-66. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.6.11
Sarowar G., Ahmed I., Rahman S., Al Mamun A., Salim K.M. Investigation of a power factor correction converter utilizing SEPIC topology with input current switching. Results in Engineering, 2024, vol. 22, art. no. 102271. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102271.
Pallekonda A.K., Ch R.K. High gain interleaved PFC converter for torque ripple minimization in industrial PMBLDC motor based drives. Results in Engineering, 2024, vol. 23, art. no. 102413. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102413.
Bushra E., Zeb K., Ahmad I., Khalid M. A comprehensive review on recent trends and future prospects of PWM techniques for harmonic suppression in renewable energies based power converters. Results in Engineering, 2024, vol. 22, art. no. 102213. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102213.
Pirashanthiyah L., Edirisinghe H.N., De Silva W.M.P., Bolonne S.R.A., Logeeshan V., Wanigasekara C. Design and Analysis of a Three-Phase Interleaved DC-DC Boost Converter with an Energy Storage System for a PV System. Energies, 2024, vol. 17, no. 1, art. no. 250. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en17010250.
Oliver J.S., David P.W., Balachandran P.K., Mihet-Popa L. Analysis of Grid-Interactive PV-Fed BLDC Pump Using Optimized MPPT in DC–DC Converters. Sustainability, 2022, vol. 14, no. 12, art. no. 7205. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127205.
Srividya S., Praveena A., TatiReddy Ravi, SathishKumar K. Single Switch DC-DC Boost Converter with MPPT Control for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Applications. 2023 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), 2023, pp. 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/i-PACT58649.2023.10434573.
Romashko V.Y., Batrak L.M., Abakumova O.O. Step-up/step-down regulators in maximum power transmission mode. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2022, no. 2, pp. 18-22. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2022.2.03.
Huang L. Reduced-order discrete modeling method and nonlinear analysis of a discontinuous conduction mode buck converter with a constant power load. Energy Reports, 2023, vol. 9, pp. 1021-1036. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2023.04.133.
Serra F.M., Esteban F.D., Montoya O.D. Control of DC-DC boost converter in discontinuous conduction mode feeding a constant power load. Results in Engineering, 2024, vol. 23, art. no. 102732. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102732.
Veeramraju K.J., Eisen J., Rovey J.L., Kimball J.W. A New Discontinuous Conduction Mode in a Transformer Coupled High Gain DC-DC Converter. 2022 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), 2022, pp. 237-244. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/APEC43599.2022.9773417.
Madrid E., Murillo-Yarce D., Restrepo C., Muñoz J., Giral R. Modelling of SEPIC, Ćuk and Zeta Converters in Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Performance Evaluation. Sensors, 2021, vol. 21, no. 22, art. no. 7434. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227434.
Parada Salado J.G., Herrera Ramírez C.A., Soriano Sánchez A.G., Rodríguez Licea M.A. Nonlinear Stabilization Controller for the Boost Converter with a Constant Power Load in Both Continuous and Discontinuous Conduction Modes. Micromachines, 2021, vol. 12, no. 5, art. no. 522. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12050522.
González I., Sánchez-Squella A., Langarica-Cordoba D., Yanine-Misleh F., Ramirez V. A PI + Sliding-Mode Controller Based on the Discontinuous Conduction Mode for an Unidirectional Buck–Boost Converter with Electric Vehicle Applications. Energies, 2021, vol. 14, no. 20, art. no. 6785. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en14206785.
Goncharov Y.P., Budonny O.V., Morozov V.G., Panasenko M.V, Romashko V.Y., Rudenko V.S. Peretovyuvalna technicala. Navchalnyi posibnyk. Chastyna 2 [Power conversion equipment. Tехt book. Part 2]. Kharkiv, Folіo Publ., 2000. 360 p. (Ukr).
Serra F.M., Magaldi G.L., Martin Fernandez L.L., Larregay G.O., De Angelo C.H. IDA-PBC controller of a DC-DC boost converter for continuous and discontinuous conduction mode. IEEE Latin America Transactions, 2018, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 52-58. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TLA.2018.8291454.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 V. Y. Romashko, L. M. Batrak

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




