Online detection of phase resistance of switched reluctance motor by sinusoidal signal injection
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.2.01Keywords:
parameter identification, signal injection, switched reluctance motorAbstract
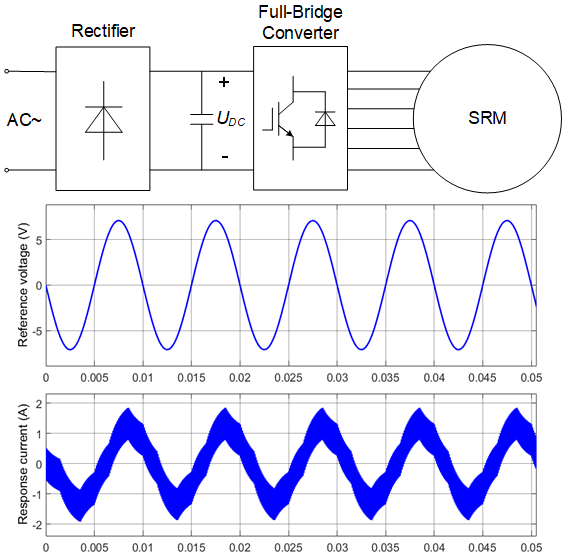
Introduction. Switched reluctance motors (SRMs) are widely used in various applications due to their simplicity, robustness, and cost-effectiveness. However, the performance of SRMs can be significantly influenced by variations in their phase resistance, especially under high current and saturated conditions. Accurate knowledge of this parameter is crucial for optimal control and efficient operation. Problem. During operation, SRM parameters, particularly phase resistance, can vary considerably. These variations pose challenges to control strategies that rely on precise parameter values, leading to potential inefficiencies and degraded performance. There is a need for an effective method to monitor and identify these changes in real-time. Goal. This paper aims to develop and validate a method for the online detection and identification of phase resistance in SRMs. The method should work under varying operational conditions without requiring additional hardware, thereby maintaining the system's simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Methodology. The proposed method injects a sinusoidal signal into the inactive phase of the SRM using Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM) via the main converter. The phasor method is then applied to determine the impedance of the phase circuit, from which the phase resistance can be identified. This approach eliminates the need for extra circuits, making it an efficient solution. Results. Simulations were conducted to evaluate the proposed method. The results demonstrate that the method can accurately track the variation in phase resistance under different operational conditions, validating its effectiveness. Originality. The originality of this work lies in its innovative use of the phasor method combined with SPWM for online phase resistance detection in SRMs, without the need for additional hardware components. Practical value. This method provides a practical solution for real-time phase resistance identification in SRMs, enhancing the reliability and performance of control strategies in various industrial applications. References 17, table 1, figures 6.
References
Fan J., Lee Y. Sensorless control of switched reluctance motor based on a simple flux linkage model. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 3, pp. 36-39. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.3.05.
Quraan L.A., Saleh A.L., Szamel L. Indirect Instantaneous Torque Control for Switched Reluctance Motor Based on Improved Torque Sharing Function. IEEE Access, 2024, vol. 12, pp. 11810-11821. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3355389.
Kumar P., Israyelu M., Sashidhar S. A Simple Four-Phase Switched Reluctance Motor Drive for Ceiling Fan Applications. IEEE Access, 2023, no. 11, pp. 7021-7030. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3238068.
Fan J., Lee Y. Design Consideration to Achieve Wide-Speed-Range Operation in a Switched Reluctance Motor. Canadian Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2020, vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 290-294. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CJECE.2020.2978265.
Sree P.B., Bhavani N.P.G. Efficiency Improvement of Electrical Vehicles Using Novel Switched Reluctance Motor and Compared with Permanent Magnet Motor by Reducing Power Loss. 2023 6th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), 2023, pp. 1473-1477. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IC3I59117.2023.10398050.
Omar M., Bakr M., Emadi A. Switched Reluctance Motor Design Optimization: A Framework for Effective Machine Learning Algorithm Selection and Evaluation. 2024 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), 2024, pp. 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ITEC60657.2024.10598839.
Omar M., Sayed E., Abdalmagid M., Bilgin B., Bakr M.H., Emadi A. Review of Machine Learning Applications to the Modeling and Design Optimization of Switched Reluctance Motors. IEEE Access, 2022, vol. 10, pp. 130444-130468. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3229043.
Kandhasamy S. Machine learning based SRM control using FPGAs for torque ripple minimization. 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), 2020, pp. 675-680. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAIIC48513.2020.9065241.
Jha M.K., Seth N., Tyagi N., Khan S.A. SRM Torque Ripple Reduction Using Grey Wolf and Teaching and Learning Based optimization in Hysteresis Control. 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), 2021, pp. 1-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CONIT51480.2021.9498374.
Matschek J., Bethge J., Findeisen R. Safe Machine-Learning-Supported Model Predictive Force and Motion Control in Robotics. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2023, vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 2380-2392. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCST.2023.3262987.
Unluturk A., Aydogdu O. Machine Learning Based Self-Balancing and Motion Control of the Underactuated Mobile Inverted Pendulum With Variable Load. IEEE Access, 2022, vol. 10, pp. 104706-104718. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3210540.
Kolb J., Hameyer K. Classification of Tolerances in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines With Machine Learning. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2024, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 831-838. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2023.3340337.
Ki Hong S., Lee Y. Optimizing Detection: Compact MobileNet Models for Precise Hall Sensor Fault Identification in BLDC Motor Drives. IEEE Access, 2024, vol. 12, pp. 77475-77485. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3407766.
Mohanraj D., Aruldavid R., Verma R., Sathiyasekar K., Barnawi A.B., Chokkalingam B., Mihet-Popa L. A Review of BLDC Motor: State of Art, Advanced Control Techniques, and Applications. IEEE Access, 2022, vol. 10, pp. 54833-54869. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3175011.
Zhang S., Wallscheid O., Porrmann M. Machine Learning for the Control and Monitoring of Electric Machine Drives: Advances and Trends. IEEE Open Journal of Industry Applications, 2023, vol. 4, pp. 188-214. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/OJIA.2023.3284717.
Mousmi A., Abbou A., El Houm Y. Binary Diagnosis of Hall Effect Sensors in Brushless DC Motor Drives. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 3859-3868. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2019.2934794.
Huang Y., Zhao M., Zhang J., Lu M. The Hall Sensors Fault-Tolerant for PMSM Based on Switching Sensorless Control With PI Parameters Optimization. IEEE Access, 2022, vol. 10, pp. 114048-114059. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3218325.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Y. Lee

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




