Brushless DC motor drive with optimal fractional-order sliding-mode control based on a genetic algorithm
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.2.03Keywords:
fractional order sliding mode control, brushless DC motor, genetic algorithm, sliding mode controllerAbstract
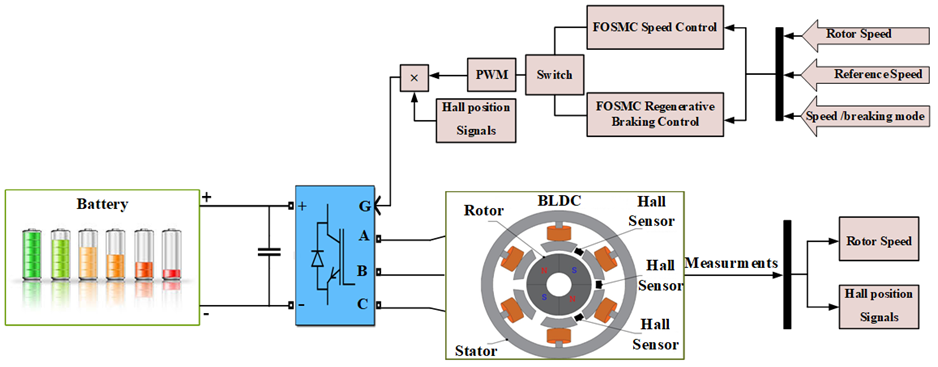
Introduction. Brushless DC (BLDC) motor is a type of permanent magnet synchronous motor that operates without brushes employed in many applications owing to its efficiency and control in electric cars. One of the main reasons BLDC motors are better than brushed DC motors is that they employ an electronic commutation circuit instead of a mechanical one. The fractional order sliding mode controller (FOSMC) was used, which is characterized by high durability and is not affected by the disturbances that the motor is exposed to during operation, as well as overcoming the chattering phenomenon present in the conventional sliding mode controller (CSMC). The novelty of the proposed work consists of to use FOSMC by genetic algorithm (GA) to mitigate the chattering phenomena in sliding mode control (SMC) for optimal response for speed control and regeneration braking control in BLDC motor by using single stage by voltage source inverter and decrease energy use during motor starting. Purpose. Improvement FOSMC techniques for the regulation of BLDC motor’s driving control system. Methods. Employing the GA to optimize the parameters of FOSMC to mitigate the chattering phenomenon in SMC to regulate BLDC motor’s driving control system. Results. A comparison was made between two types of sliding controllers to obtain the best performance of the control system in speed control operations and motor braking operations, the FOSMC, through parameter optimization via the GA, surpasses the CSMC in achieving optimal performance in driving the BLDC motor. Practical value. FOSMC exhibits superiority over the CSMC, as indicated by the reduced integral time absolute error in motor speed tracking and regenerative brake control, with values of (0.028, 0.046, and 0.075) for the FOSMC, in contrast to (2.72, 1.56, and 0.17) for the CSMC, the overshoot for FOSMC is (0, 0, and 11.4), but for CSMC it is (60.4, 43.7, and 11.2). During braking mode for FOSMC, the power recovery from the motor to the battery was (1.96, 9, and 17.76), but in CSMC, it was (0.99, 4.49, and 11.98). Moreover, the braking length was expedited, and the battery’s initial power consumption diminished at the outset. References 32, tables 5, figures 6.
References
Saiteja P., Ashok B., Mason B., Kumar P.S. Assessment of Adaptive Self-Learning-Based BLDC Motor Energy Management Controller in Electric Vehicles Under Real-World Driving Conditions for Performance Characteristics. IEEE Access, 2024, vol. 12, pp. 40325-40349. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3375753.
Mohanraj D., Aruldavid R., Verma R., Sathiyasekar K., Barnawi A.B., Chokkalingam B., Mihet-Popa L. A Review of BLDC Motor: State of Art, Advanced Control Techniques, and Applications. IEEE Access, 2022, vol. 10, pp. 54833-54869. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3175011.
Patel A.N. Slot opening displacement technique for cogging torque reduction of axial flux brushless DC motor for electric two-wheeler application. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 2, pp. 7-13. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.2.02.
Prabhu N., Thirumalaivasan R., Ashok B. Design of sliding mode controller with improved reaching law through self-learning strategy to mitigate the torque ripple in BLDC motor for electric vehicles. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2024, vol. 118, art. no. 109438. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2024.109438.
Akrami M., Jamshidpour E., Nahid-Mobarakeh B., Pierfederici S., Frick V. Sensorless Control Methods for BLDC Motor Drives: A Review. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2024, pp. 1–1. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2024.3387371.
Saha B., Singh B. Torque Ripple Mitigation in Sensorless PMBLDC Motor Drive With Adaptive Observer for LEV. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2025, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 1739-1747. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2024.3457677.
Khemis A., Boutabba T., Drid S. Model reference adaptive system speed estimator based on type-1 and type-2 fuzzy logic sensorless control of electrical vehicle with electrical differential. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 4, pp. 19-25. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.4.03.
Lee H.-Y., Cha K.-S., Kwon S.-O., Yoon S.-Y., Seok C.-H., Lim M.-S. Efficiency Analysis of BLDC Motor With Delta Connection According to Magnitude of Circulating Current. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2024, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 1-5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2024.3465879.
Sakri D., Laib H., Farhi S.E., Golea N. Sliding mode approach for control and observation of a three phase AC-DC pulse-width modulation rectifier. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 2, pp. 49-56. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.2.08.
Mohammed H.A., Alsammak A.N.B. An Intelligent Hybrid Control System using ANFIS-Optimization for Scalar Control of an Induction Motor. Journal Européen Des Systèmes Automatisés, 2023, vol. 56, no. 5, pp. 857-862. doi: https://doi.org/10.18280/jesa.560516.
Li K., Ding J., Sun X., Tian X. Overview of Sliding Mode Control Technology for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor System. IEEE Access, 2024, vol. 12, pp. 71685-71704. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3402983.
Ibrahim M.A., Alsammak A.N.B. Adaptive PID Control for 8/6 Switched Reluctance Motor Drive Based on BFO. Journal Européen Des Systèmes Automatisés, 2023, vol. 56, no. 4, pp. 539-546. doi: https://doi.org/10.18280/jesa.560403.
Ibrahim M.A., Alsammak A.N.B. Switched Reluctance Motor Drives Speed Control Using Optimized PID Controller. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 2022, vol. 98, no. 11, pp. 46-50. doi: https://doi.org/10.15199/48.2022.11.7.
Alnaib I.I., Alsammak A.N. Optimization of fractional PI controller parameters for enhanced induction motor speed control via indirect field-oriented control. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2025, no. 1, pp. 3-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.1.01.
Younus S.M.Y., Kutbay U., Rahebi J., Hardalaç F. Hybrid Gray Wolf Optimization–Proportional Integral Based Speed Controllers for Brush-Less DC Motor. Energies, 2023, vol. 16, no. 4, art. no. 1640. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041640.
Ok S., Xu Z., Lee D.-H. A Sensorless Speed Control of High-Speed BLDC Motor Using Variable Slope SMO. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2024, vol. 60, no. 2, pp. 3221-3228. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2023.3348081.
Kheel A.M., Al-Shamaa N.K., Hawas M.N. Sliding Mode Controller Enchancement for Speed Control of BLDC Motor Based On Dragonfly Algorithm. 2023 International Conference on Converging Technology in Electrical and Information Engineering (ICCTEIE), 2023, pp. 135-141. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCTEIE60099.2023.10366754.
Basci A., Derdiyok A., Can K., Orman K. A Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Controller Design for Trajectory Tracking Control of An Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Elektronika Ir Elektrotechnika, 2020, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 4-10. doi: https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.eie.26.4.25846.
El Idrissi A.L., Bouchnaif J., Mokhtari M., Bensliman A. Comparative study between pi speed control and sliding mode control of bldc motor. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, 2020, vol. 684 LNEE, pp. 309-317. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-53187-4_35.
Soni N., Barai M. Performance Study of Regenerative Braking of BLDC Motor targeting Electric Vehicle Applications. 2022 2nd Asian Conference on Innovation in Technology (ASIANCON), 2022, pp. 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ASIANCON55314.2022.9909322.
Saha B., Singh B., Sen A. SMO Based Position Sensorless BLDC Motor Drive Employing Canonical Switching Cell Converter for Light Electric Vehicle. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2023, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 2974-2984. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2023.3241607.
Prabhu N., Thirumalaivasan R., Ashok B. Critical Review on Torque Ripple Sources and Mitigation Control Strategies of BLDC Motors in Electric Vehicle Applications. IEEE Access, 2023, vol. 11, pp. 115699-115739. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3324419.
Azab M. Comparative Study of BLDC Motor Drives with Different Approaches: FCS-Model Predictive Control and Hysteresis Current Control. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 2022, vol. 13, no. 7, art. no. 112. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj13070112.
Bazi S., Benzid R., Bazi Y., Rahhal M.M.Al. A Fast Firefly Algorithm for Function Optimization: Application to the Control of BLDC Motor. Sensors, 2021, vol. 21, no. 16, art. no. 5267. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165267.
Ullah A., Pan J., Ullah S., Zhang Z. Robust Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive System Using Sliding-Mode Disturbance Observer-Based Variable-Gain Fractional-Order Super-Twisting Sliding-Mode Control. Fractal and Fractional, 2024, vol. 8, no. 7, art. no. 368. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8070368.
Mohd Zaihidee F., Mekhilef S., Mubin M. Robust Speed Control of PMSM Using Sliding Mode Control (SMC) – A Review. Energies, 2019, vol. 12, no. 9, art. no. 1669. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en12091669.
Lin X., Liu J., Liu F., Liu Z., Gao Y., Sun G. Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Approach of Buck Converters With Mismatched Disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2021, vol. 68, no. 9, pp. 3890-3900. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2021.3092138.
Zaihidee F.M., Mekhilef S., Mubin M. Application of Fractional Order Sliding Mode Control for Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Access, 2019, vol. 7, pp. 101765-101774. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931324.
Zhao B., Chen W.-N., Wei F.-F., Liu X., Pei Q., Zhang J. PEGA: A Privacy-Preserving Genetic Algorithm for Combinatorial Optimization. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, vol. 54, no. 6, pp. 3638-3651. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2023.3346863.
Patel A.N., Suthar B.N. Performance optimisation of axial flux permanent magnet brushless DC motor for electric vehicle application with the genetic algorithm (GA) approach. International Journal of Ambient Energy, 2024, vol. 45, no. 1, art. no. 2370850. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2024.2370850.
Baszynski M., Pirog S. Unipolar Modulation for a BLDC Motor With Simultaneously Switching of Two Transistors With Closed Loop Control for Four-Quadrant Operation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 146-155. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2017.2723962.
Mishra A.K., Singh A.K., Vishwanath G.M. A Fuel-Efficient BLDC Motor-Driven Light Electric Vehicle With Single-Stage Onboard Charging System. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2023, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 4909-4921. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2022.3226536.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 I. I. Alnaib, A. N. Alsammak, K. K. Mohammed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




