Global maximum power point tracking method for photovoltaic systems using Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy models and ANFIS approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.2.05Keywords:
photovoltaic system, maximum power point tracking, Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model, linear matrix inequalitiesAbstract
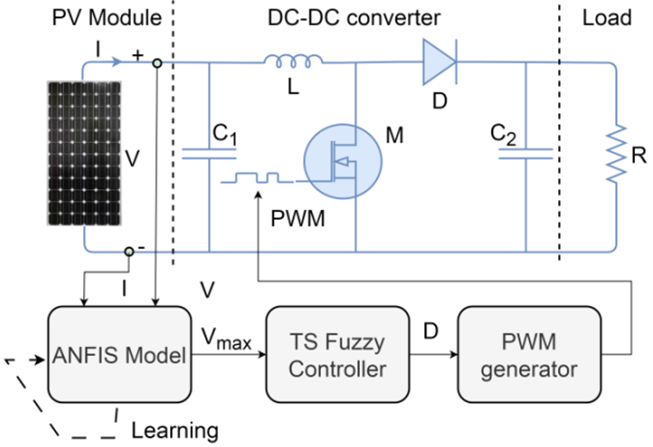
Introduction. A new global maximum power point tracking (GMPPT) control strategy for a solar photovoltaic (PV) system, based on the combination of Takagi-Sugeno (T-S) fuzzy models and an ANFIS, is presented. The novelty of this paper lies in the integration of T-S fuzzy models and the ANFIS approach to develop an efficient GMPPT controller for a PV system operating under partial shading conditions. Purpose. The new GMPPT control strategy aims to extract maximum power from the PV system under varying weather conditions or partial shading. Methods. An ANFIS algorithm is used to determine the maximum voltage, which corresponds to the actual maximum power point, based on PV voltage and current. Next, the nonlinear model of the PV system is employed to design the T-S fuzzy controller. A reference model is then derived based on the maximum voltage. Finally, a tracking controller is developed using the reference model and the T-S fuzzy controller. The stability of the overall system is evaluated using Lyapunov’s method and is represented through linear matrix inequalities expressions. The results clearly demonstrate the advantages of the proposed GMPPT-based fuzzy control strategy, showcasing its high performance in effectively reducing oscillations in various steady states of the PV system, ensuring minimal overshoot and a faster response time. In addition, a comparative analysis of the proposed GMPPT controller against conventional algorithms, such as Incremental Conductance, Perturb & Observe and Particle Swarm Optimization, shows that it offers a fast dynamic response in finding the maximum power with significantly less oscillation around the maximum power point. References 20, tables 3, figures 14.
References
Chen X.H., Tee K., Elnahass M., Ahmed R. Assessing the environmental impacts of renewable energy sources: A case study on air pollution and carbon emissions in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, vol. 345, art. no. 118525. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118525.
Osman A.I., Chen L., Yang M., Msigwa G., Farghali M., Fawzy S., Rooney D.W., Yap P.-S. Cost, environmental impact, and resilience of renewable energy under a changing climate: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2023, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 741-764. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01532-8.
Youcef H., Touhami G., Omar O., Essama G.A., Slimane L. Sliding Mode based PSO MPPT for Solar PV System. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 2024, no. 1, pp. 86-90. doi: https://doi.org/10.15199/48.2024.01.18.
Juma’a H.G., Atyia T.H. Design a 91-Multilevel Inverter Circuit Using Solar PV System Sources. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 2023, no. 11, pp. 127-133. doi: https://doi.org/10.15199/48.2023.11.22.
Paquianadin V., Navin Sam K., Koperundevi G. Maximizing solar photovoltaic system efficiency by multivariate linear regression based maximum power point tracking using machine learning. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2024, no. 1, pp. 77-82. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2024.1.10.
Guiza D., Ounnas D., Soufi Y., Bouden A., Maamri M. Implementation of Modified Perturb and Observe Based MPPT Algorithm for Photovoltaic System. 2019 1st International Conference on Sustainable Renewable Energy Systems and Applications (ICSRESA), 2019, pp. 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSRESA49121.2019.9182483.
Zerzouri N., Ben Si Ali N., Benalia N. A maximum power point tracking of a photovoltaic system connected to a three-phase grid using a variable step size perturb and observe algorithm. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, vol. 5, pp. 37-46. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.5.06.
Dhaouadi G., Djamel O., Youcef S., Salah C. Implementation of Incremental Conductance Based MPPT Algorithm for Photovoltaic System. 2019 4th International Conference on Power Electronics and Their Applications (ICPEA), 2019, pp. 1-5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPEA1.2019.8911186.
Louarem S., Kebbab F.Z., Salhi H., Nouri H. A comparative study of maximum power point tracking techniques for a photovoltaic grid-connected system. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2022, no. 4, pp. 27-33. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2022.4.04.
Jately V., Azzopardi B., Joshi J., Balaji Venkateswaran V., Sharma A., Arora S. Experimental analysis of hill-climbing MPPT algorithms under low irradiance levels. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, vol. 150, art. no. 111467. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111467.
Ounnas D., Guiza D., Soufi Y., Maamri M. Design and Hardware Implementation of Modified Incremental Conductance Algorithm for Photovoltaic System. Advances in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2021, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 100-111. doi: https://doi.org/10.15598/aeee.v19i2.3881.
Wang Q., Chang X. Maximum Power Point Tracking of PV System Under Partial Shading Conditions Based on TSO-IP&O Algorithm. 2023 3rd International Conference on Energy, Power and Electrical Engineering (EPEE), 2023, pp. 155-159. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EPEE59859.2023.10351794.
Chaibi R., Bachtiri R.E., Hammoumi K.E., Yagoubi M. Photovoltaic System’s MPPT Under Partial Shading Using T-S Fuzzy Robust Control. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2022, vol. 55, no. 12, pp. 214-221. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2022.07.314.
Moussaoui L., Aouaouda S., Rouaibia R. Fault tolerant control of a permanent magnet synchronous machine using multiple constraints Takagi-Sugeno approach. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2022, no. 6, pp. 22-27. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2022.6.04.
Guiza D., Soufi Y., Ounnas D., Metatla A. Design and Implementation of Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Tracking Control for a DC-DC Buck Converter. Advances in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2019, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 234-243. doi: https://doi.org/10.15598/aeee.v17i3.3126.
Sekhar P.C., Mishra S. Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy‐based incremental conductance algorithm for maximum power point tracking of a photovoltaic generating system. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2014, vol. 8, no. 8, pp. 900-914. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2013.0219.
Ounnas D., Ramdani M., Chenikher S., Bouktir T. An Efficient Maximum Power Point Tracking Controller for Photovoltaic Systems Using Takagi–Sugeno Fuzzy Models. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2017, vol. 42, no. 12, pp. 4971-4982. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2532-0.
Kahsay A.H., Regulski P., Derugo P. AI-based control techniques for maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic systems using a boost converter. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 2023, no. 11, pp. 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.15199/48.2023.11.01.
Ohtake H., Tanaka K., Wang H.O. Fuzzy modeling via sector nonlinearity concept. Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, 2003, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 333-341. doi: https://doi.org/10.3233/ICA-2003-10404.
Ounnas D., Ramdani M., Chenikher S., Bouktir T. Optimal reference model based fuzzy tracking control for wind energy conversion system. International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, 2016, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 1129-1136. doi: https://doi.org/10.20508/ijrer.v6i3.4258.g6896.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 N. Hadjidj, M. Benbrahim, D. Ounnas, L. H. Mouss

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




