Integrating dual active bridge DC-DC converters: a novel energy management approach for hybrid renewable energy systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.2.06Keywords:
hybrid renewable energy system, dual active bridge DC-DC converter, energy management strategy, maximum power point trackingAbstract
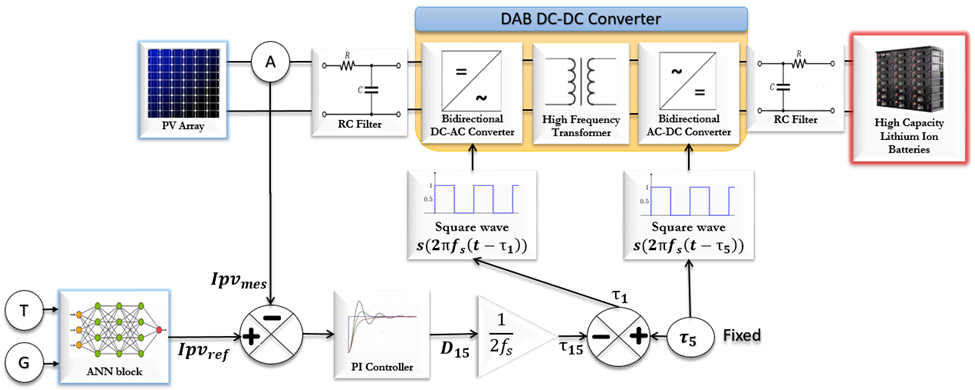
Introduction. Hybrid renewable energy systems, which integrate wind turbines, solar PV panels, and battery storage, are essential for sustainable energy solutions. However, managing the energy flow in these systems, especially under varying load demands and climatic conditions, remains a challenge. The novelty of this paper is introduces a hybrid renewable energy system structure using Dual Active Bridge (DAB) DC-DC converters and an energy management strategy (EMS) to control power flow more effectively. The approach includes a dump load mechanism to handle excess energy, offering a more efficient and flexible system operation. The purpose of this study is to develop a novel approach to managing and controlling hybrid renewable energy systems, specifically through the use of a DAB DC-DC converter. Unlike traditional methods that may struggle with efficiency and flexibility, our approach introduces an innovative EMS that leverages a reduced neural network block for real-time optimal power tracking and a sophisticated control system to adapt to dynamic conditions. This approach aims to improve the flexibility of the system, enhance energy utilization, and address the limitations of existing methods by ensuring rapid and efficient responses to changes in load and climatic conditions. The primary goal of this study is to improve the performance and reliability of hybrid renewable energy systems by optimizing energy distribution and battery management. The strategy aims to ensure continuous energy availability, enhance battery lifespan, and improve system response to dynamic changes. Methods. The proposed EMS was developed and tested using MATLAB/Simulink. The system’s control mechanism prioritizes battery charging when renewable energy output exceeds demand and redirects excess energy to a dump load when necessary. Simulations were conducted under various load and climatic conditions to assess system performance. Results. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed strategy effectively manages energy flow, ensuring optimal power distribution, quick adaptation to load changes, and maintaining the battery’s state of charge within safe limits. Practical value. The system showed improved stability and efficiency, validating the effectiveness of the control strategy in enhancing the overall performance of hybrid renewable energy systems. References 33, tables 3, figures 13.
References
Das S., Akella A.K. Power Flow Control of PV-Wind-Battery Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems for Stand-Alone Application. International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, 2018, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 36-43. doi: https://doi.org/10.20508/ijrer.v8i1.6534.g7278.
Lu J., Siaw F.L., Thio T.H.G., Wang J.J. Capacity optimization of independent hybrid renewable energy system under different operational strategies based on improved gray wolf algorithm. AIP Advances, 2024, vol. 14, no. 5, art. no. 055205. pp. doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0198446.
Gajewski P., Pieńkowski K. Control of the Hybrid Renewable Energy System with Wind Turbine, Photovoltaic Panels and Battery Energy Storage. Energies, 2021, vol. 14, no. 6, art. no. 1595. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en14061595.
Vinothkumar J., Thamizhselvan R. Efficient Power Management and Control Strategy of Hybrid Renewable Energy System in Microgrid. International Journal on Applied Physics and Engineering, 2023, vol. 2, pp. 106-127. doi: https://doi.org/10.37394/232030.2023.2.11.
Jamal S., Pasupuleti J., Ekanayake J. A rule-based energy management system for hybrid renewable energy sources with battery bank optimized by genetic algorithm optimization. Scientific Reports, 2024, vol. 14, no. 1, art. no. 4865. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-54333-0.
Ayat Y., Badoud A.E., Mekhilef S., Gassab S. Energy management based on a fuzzy controller of a photovoltaic/fuel cell/Li-ion battery/supercapacitor for unpredictable, fluctuating, high-dynamic three-phase AC load. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 3, pp. 66-75. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.3.10.
Bourouis B., Djeghloud H., Benalla H. An innovative algorithm for a hybrid fc/battery system energy management. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2020, no. 6, pp. 35-44. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2020.6.06.
Tahiri F.E., Chikh K., Khafallah M. Optimal Management Energy System and Control Strategies for Isolated Hybrid Solar-Wind-Battery-Diesel Power System. Emerging Science Journal, 2021, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 111-124. doi: https://doi.org/10.28991/esj-2021-01262.
Ndeke C.B., Adonis M., Almaktoof A. Energy management strategy for a hybrid micro-grid system using renewable energy. Discover Energy, 2024, vol. 4, no. 1, art. no. 1. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43937-024-00025-9.
Iqbal M.M., Kumar S., Lal C., Kumar C. Energy management system for a small-scale microgrid. Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology, 2022, vol. 9, no. 1, art. no. 5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43067-022-00046-1.
Maaruf M., Khan K., Khalid M. Robust Control for Optimized Islanded and Grid-Connected Operation of Solar/Wind/Battery Hybrid Energy. Sustainability, 2022, vol. 14, no. 9, art. no. 5673. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095673.
Cabrane Z., Lee S.H. Control and Management of Railway System Connected to Microgrid Stations. IEEE Access, 2022, vol. 10, pp. 40445-40455. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3165832.
Mechnane F., Drid S., Nait-Said N., Chrifi-Alaoui L. Robust Current Control of a Small-Scale Wind–Photovoltaic Hybrid System Based on the Multiport DC Converter. Applied Sciences, 2023, vol. 13, no. 12, art. no. 7047. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127047.
Moghaddam S., Bigdeli M., Moradlou M. Optimal design of an off-grid hybrid renewable energy system considering generation and load uncertainty: the case of Zanjan city, Iran. SN Applied Sciences, 2021, vol. 3, no. 8, art. no. 732. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04718-x.
Menzri F., Boutabba T., Benlaloui I., Khamari D. Optimization of Energy management using a particle swarm optimization for hybrid renewable energy sources. 2022 2nd International Conference on Advanced Electrical Engineering (ICAEE), 2022, pp. 1-5. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAEE53772.2022.9962065.
Jafari M., Malekjamshidi Z. A Topology of DC-DC Converter Based on Multi-Winding Transformer for Grid Integration of Multiple Renewable Energy Resources. Inventions, 2020, vol. 5, no. 3, art. no. 31. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions5030031.
Dong Z., Yang P., Li Q., Zhang M., Chang Y., Wang S. Fractional order modelling and optimal control of dual active bridge converters. Systems Science & Control Engineering, 2024, vol. 12, no. 1, art. no. 2347886. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/21642583.2024.2347886.
Effah E.K., Anto E.K., Okyere P.Y., Effah F.B. Model Reference Adaptive Control of SPS-Based Dual Active Bridge Converter with Constant Power Loading. Power Electronics and Drives, 2024, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 348-357. doi: https://doi.org/10.2478/pead-2024-0022.
Henao-Bravo E.E., Ramos-Paja C.A., Saavedra-Montes A.J., González-Montoya D., Sierra-Pérez J. Design Method of Dual Active Bridge Converters for Photovoltaic Systems with High Voltage Gain. Energies, 2020, vol. 13, no. 7, art. no. 1711. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071711.
Hessad M.A., Bouchama Z., Benaggoune S., Behih K. Cascade sliding mode maximum power point tracking controller for photovoltaic systems. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 1, pp. 51-56. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.1.07.
Chen Q., Wang L., Sun Y., Xie S., Wang R. Adaptive integral sliding mode MPPT control for wind turbines with fixed‐time convergence. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2024, vol. 18, no. S1, pp. 4265-4276. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/rpg2.12935.
Bahri M., Talea M., Bahri H., Aboulfatah M. An efficient scanning algorithm for photovoltaic systems under partial shading. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE), 2022, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 5799-5807. doi: https://doi.org/10.11591/ijece.v12i6.pp5799-5807.
Bendib D., Laour M. Modified incremental conductance MPPT using SEPIC converter for PV system, simulation and Arduino implementation. Studies in Engineering and Exact Sciences, 2024, vol. 5, no. 2, art. no. e6614. doi: https://doi.org/10.54021/seesv5n2-090.
Benhacine T.Z., Dali A., Tata M., Kherbachi A., Boudraf M., Kaabeche A. Design of a test bench for a small wind turbine emulator. Journal of Renewable Energies, 2024, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 5-13. doi: https://doi.org/10.54966/jreen.v27i1.1113.
Abo-Khalil A.G., Alobaid M. Optimized Control for PMSG Wind Turbine Systems under Unbalanced and Distorted Grid Voltage Scenarios. Sustainability, 2023, vol. 15, no. 12, art. no. 9552. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129552.
Ríos S.J., Pagano D.J., Lucas K.E. Bidirectional Power Sharing for DC Microgrid Enabled by Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converter. Energies, 2021, vol. 14, no. 2, art. no. 404. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en14020404.
Sabhi K., Talea M., Bahri H. Improving Power Precision in Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems with a Quad Active Bridge DC-DC Converter and Neural Network-Based Decoupling. 2024 International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Computer Vision (ISCV), 2024, pp. 1-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCV60512.2024.10620155.
Mahamat C., Bechet J., Linguet L. Artificial Neural Network Control Applied to a Photovoltaic-Battery Microgrid System. AI, Computer Science and Robotics Technology, 2024, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 1-20. doi: https://doi.org/10.5772/acrt.34.
Vamsi Krishna A., Sateesh B., Sai Sankar M., Sravanthi P., Vanaja Suvarna P., Devendra Goud E. A novel MPPT method for a standalone PV System. International Journal for Modern Trends in Science and Technology, 2024, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 60-66. doi: https://doi.org/10.46501/IJMTST1004010.
Bana P.R., D’Arco S., Amin M. ANN-Based Robust Current Controller for Single-Stage Grid-Connected PV With Embedded Improved MPPT Scheme. IEEE Access, 2024, vol. 12, pp. 100251-100262. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3429347.
Hichem L., Leila M., Amar O. The effectiveness of a hybrid MPPT controller based on an artificial neural network and fuzzy logic in low-light conditions. Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, 2024, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 1453-1464. doi: https://doi.org/10.11591/eei.v13i3.6416.
Costanzo L., Rubino G., Rubino L., Vitelli M. PFC Control Signal Driven MPPT Technique for Grid-Connected PV Systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2024, vol. 39, no. 8, pp. 10368-10379. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2024.3393294.
Jasim A.M., Jasim B.H., Bureš V. A novel grid-connected microgrid energy management system with optimal sizing using hybrid grey wolf and cuckoo search optimization algorithm. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2022, vol. 10, art. no. 960141. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2022.960141.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 K. Sabhi, M. Talea, H. Bahri, S. Dani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




