Complex physicochemical analysis of transformer oil parameters using the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.2.10Keywords:
transformer oil, furfural component, breakdown voltage, mass spectrometer, dissolved gases analysisAbstract
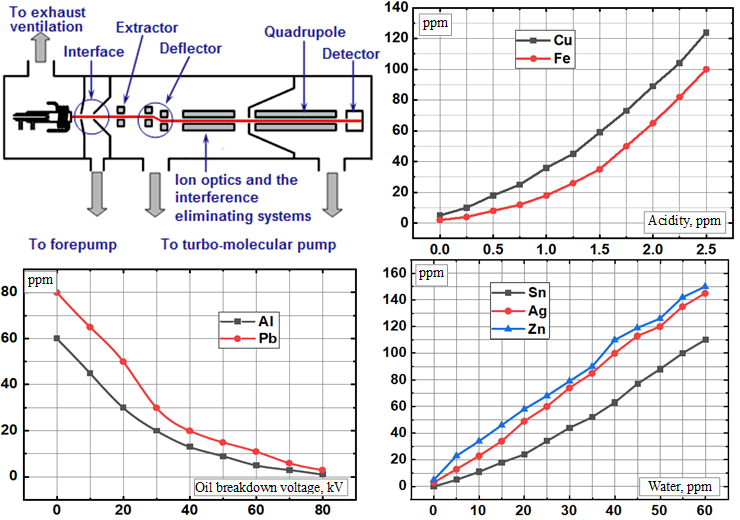
Introduction. Transformers are crucial and expensive components of power systems, experiencing electrical, thermal, and chemical stresses. Transformer oil analysis is important for diagnosing transformer faults and assessing its remaining service life. The oil used in transformers degrades over time due to its interaction with electrical loads and heat from the core and windings. The oil degrades into low-molecular gases and carbon particles, which affect its dielectric properties and indicate potential problems. Analysis of dissolved gases in oil allows early detection of defects such as corona or arc discharges, as well as overheating. In addition, analysis of metal content in oil helps to clarify the type and location of the fault identified by gas analysis. Novelty of the proposed work lies in the study of the relationship between transformer oil parameters and its quality, as well as the effect of dissolved gases. The article proposes a method for determining how changes in these parameters affect each other. The obtained data are compared with the results of mass spectrometric analysis for a more accurate assessment of the transformer condition. The purpose of this paper is to explore the connection between the chemical properties of transformer oil and the elemental composition determined through inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Methods. The solution to the problem was carried out using the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry method from Agilent Technologies 7700e (USA) to measure the concentration of metals in transformer oil. Results. An inverse correlation has been identified between the acidity of transformer oil and its furfural content. Experimental evidence has shown that the water content has the most significant impact on decreasing the breakdown voltage of dielectric oil. It was found that CO gas has the greatest influence on the formation of furfural. It has been established that gaseous C2H2 plays an important role in the formation of acidic components. Correlations were found between the oil acidity and the concentrations of copper and iron and between the breakdown voltage and the amount of lead and aluminium in the transformer oil. A high concentration of copper in the oil indicates potential issues with the transformer windings, as well as in any bronze or brass components, and the concentration of iron in significant quantities indicates problems with the transformer core and tank. Moreover, as the breakdown voltage of the oil decreases, there is a marked increase in the concentrations of lead and aluminum. This suggests that significant amounts of lead are found in the transformer solder joints, while aluminum is present in the windings and ceramic bushings. Practical value. The advantage of the mass spectrometric method for detecting metals in transformer oils is the ability to accurately determine the type of fault and diagnose transformer problems. Research shows that this method allows early detection of potential problems and predicts the condition of the transformer. References 21, table 2, figures 8.
References
Somekawa T., Fujita M., Izawa Y., Kasaoka M., Nagano Y. Furfural analysis in transformer oils using laser raman spectroscopy. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2015, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 229-231. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2014.004800.
Zhang L., Sun L., Wu J., Han Y., Wang S., Yang C., Shen W., Guo C. Development of multi‐parameter online monitoring equipment for EHV transformer bushing. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 2020, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 98-103. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-smt.2019.0262.
Faria G., Pereira M., Lopes G., Villibor J., Tavares P., Faria I. Evaluation of Capacitance and Dielectric Dissipation Factor of Distribution Transformers - Experimental Results. 2018 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC), 2018, pp. 336-339. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EIC.2018.8481052.
Lundgaard L., Hansen W., Ingebrigtsen S. Ageing of Mineral Oil Impregnated Cellulose by Acid Catalysis. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2008, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 540-546. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TDEI.2008.4483475.
Poliakov M.O., Vasylevskyi V.V. Method for assessing unevenness of cellulose insulation layers aging of power transformers winding. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2022, no. 5, pp. 47-54. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2022.5.08.
Hernanda I.G.N.S., Mulyana A.C., Asfani D.A., Negara I.M.Y., Fahmi D. Application of health index method for transformer condition assessment. TENCON 2014 - 2014 IEEE Region 10 Conference, 2014, pp. 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TENCON.2014.7022433.
Nurubeili T.K. Effect of Doubly Charged Ions in Forming the Mass Spectra of Solid-State Substances in a Mass Spectrometer with Inductively Coupled Plasma. Surface Engineering and Applied Electrochemistry, 2018, vol. 54, no. 4, pp. 395-400. doi: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068375518040142.
Nurubeyli T.K., Jafar N.S., Mammadova G.N. Improving methods for sample preparation of biological fluids by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2025, vol. 507, art. no. 117355. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2024.117355.
Ahadzade S.M., Nurubeyli T.K., Quliyev E.Z., Sultanli A.N. Technological and electrophysical parameters of ZnO varistor with impurities. International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering, 2023, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 307-311.
Nurubeyli T.K. Coefficient of Relative Sensitivity in Mass Spectrometers with Inductively Coupled Plasma. Inorganic Materials: Applied Research, 2020, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 552-557. doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113320030351.
Nurubeyli T.K., Zeynalov J.I., Mammadova G.N., Imamverdiyev N.E. Improving methods for sample preparation of transformer oils by ICP-MS. International Journal on Technical and Physical Problems of Engineering, 2024, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 21-26.
Saeid M., Zeinoddini-Meymand H., Kamel S., Khan B. Interaction of transformer oil parameters on each other and on transformer health index using curve estimation regression method. International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, 2022, vol. 2022, art. no. 7548533. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7548533.
Guo H., Guo L. Health index for power transformer condition assessment based on operation history and test data. Energy Reports, 2022, vol. 8, pp. 9038-9045. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.07.041.
Palchykov O.O. Breakdown voltage of micron range air inclusions in capacitor paper. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2020, no. 6, pp. 30-34. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2020.6.05.
Aizpurua J.I., Stewart B.G., McArthur S.D.J., Lambert B., Cross J.G., Catterson V.M. Improved power transformer condition monitoring under uncertainty through soft computing and probabilistic health index. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, vol. 85, art. no. 105530. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105530.
Zeinoddini‐Meymand H., Vahidi B. Health index calculation for power transformers using technical and economical parameters. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 2016, vol. 10, no. 7, pp. 823-830. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-smt.2016.0184.
Zhang X., Gockenbach E. Asset-Management of Transformers Based on Condition Monitoring and Standard Diagnosis [Feature Article]. IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine, 2008, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 26-40. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MEI.2008.4581371.
Chen S., Chen Y., Yu N., Pang X., Zhang L., Han Z., Feng G., Jia Y., Xu T. Aging Analysis of Transformer Mineral Insulating Oil Based on Chromatographic Furfural Content Determination. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, vol. 493, art. no. 012069. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/493/1/012069.
Vasilevskij V.V., Poliakov M.O. Reproducing of the humidity curve of power transformers oil using adaptive neuro-fuzzy systems. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2021, no. 1, pp. 10-14. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2021.1.02.
Jahromi A., Piercy R., Cress S., Service J., Fan W. An approach to power transformer asset management using health index. IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine, 2009, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 20-34. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/MEI.2009.4802595.
Costa J.V., da Silva D.F.F., Branco P.J.C. Large-Power Transformers: Time Now for Addressing Their Monitoring and Failure Investigation Techniques. Energies, 2022, vol. 15, no. 13, art. no. 4697. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en15134697.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 T. K. Nurubeyli, A. M. Hashimov, N. E. Imamverdiyev, G. N. Mammadova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




