Finite-time robust position tracking control for DC motors under uncertain dynamics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2026.1.06Keywords:
DC motor, finite-time control, sliding mode control, diffeomorphism transformation, differential geometric methodAbstract
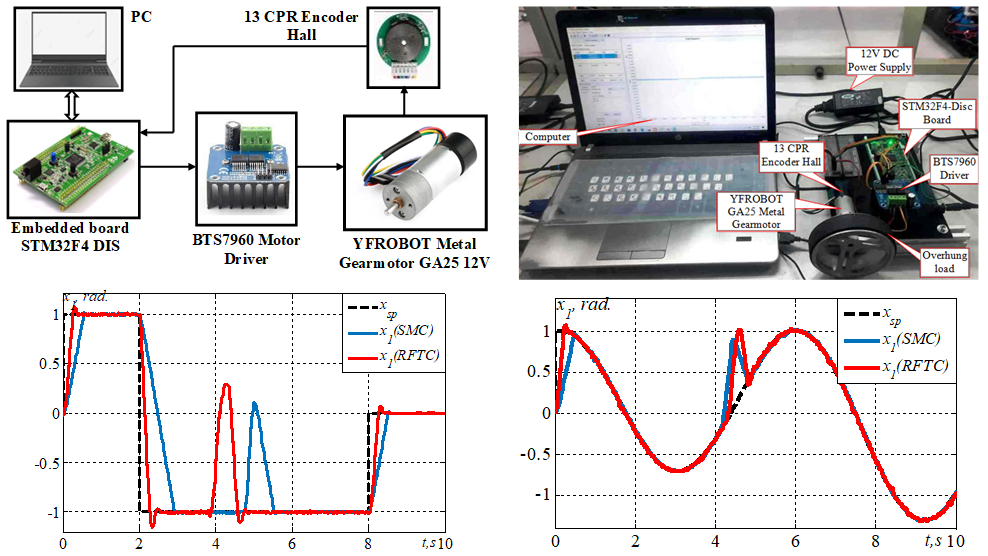
Introduction. This study proposes a finite-time robust control law for position tracking of a DC motor under conditions of model uncertainty and external disturbances. The motor operates through a pulse-width modulation (PWM) unit and an H-bridge power circuit, aiming to achieve finite-time position tracking while minimizing the effects of model uncertainties and external disturbances. Problem. The main challenge lies in achieving accurate and rapid position and speed regulation for the DC motor while maintaining high performance, despite model inaccuracies and external disturbances. The goal of this paper is to design a robust finite-time position tracking control law for a DC motor based on the differential geometric approach, ensuring high tracking accuracy and control efficiency in the presence of disturbances and parameter uncertainties. Scientific novelty. The integration of finite-time control based on a virtual system, diffeomorphism transformation, and disturbance compensation introduces an innovative solution for DC motor position tracking under incomplete modeling and external perturbations. Methodology. The study employs the differential geometric method to construct a virtual system with finite-time characteristics and uses Lyapunov theory to prove global stability in the presence of uncertainties and disturbances. A finite-time virtual system is proposed after analyzing the incomplete dynamic model of the DC motor. Results. To validate the proposed approach, MATLAB simulations were conducted and compared with a conventional sliding mode controller. The results demonstrate improved settling time and robustness of the proposed method in DC motor position tracking. The findings confirm that the proposed controller provides intuitive and precise control, accurate position tracking, and enhanced performance regulation. It also exhibits strong robustness against model uncertainties and external disturbances. The practical value of the proposed method is considerable, as it offers a reliable and efficient position control scheme for DC motors using PWM. The method ensures precise position control and robust performance under varying conditions and external interferences, making it well-suited for real-world DC motor control applications. References 23, tables 1, figures 12.
References
Weng C. DC servo motor angle control based on PID control system. IET Conference Proceedings, 2024, vol. 2024, no. 19, pp. 1-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/icp.2024.3955.
Srinivas G., Durga Sukumar G., Subbarao M. Total harmonic distortion analysis of inverter fed induction motor drive using neuro fuzzy type-1 and neuro fuzzy type-2 controllers. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2024, no. 1, pp. 10-16. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2024.1.02.
Wang X., Wang S. Adaptive Back-stepping Control of Servo Systems With Asymmetric Dead Zone. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2024, vol. 22, no. 9, pp. 2711-2722. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-024-0202-z.
Alejandro-Sanjines U., Maisincho-Jivaja A., Asanza V., Lorente-Leyva L.L., Peluffo-Ordóñez D.H. Adaptive PI Controller Based on a Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for Speed Control of a DC Motor. Biomimetics, 2023, vol. 8, no. 5, art. no. 434. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8050434.
Garcia-Chica A., Torres-Moreno J.L., Gimenez A. PID Control of DC Actuators. Consideration to Energy Robotic Design. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2024, vol. 58, no. 7, pp. 258-262. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2024.08.071.
Dawane M.K., Malwatkar G.M., Deshmukh S.P. Performance improvement of DC servo motor using sliding mode controller. Journal of Autonomous Intelligence, 2023, vol. 7, no. 3, art. no. 1162. doi: https://doi.org/10.32629/jai.v7i3.1162.
Alnaib I.I., Alsammak A.N., Mohammed K.K. Brushless DC motor drive with optimal fractional-order sliding-mode control based on a genetic algorithm. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2025, no. 2, pp. 19-23. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.2.03.
Du H., Tao L., Deng X., Xu, B. Adaptive Parameter Identification Based Tracking Control of Servo Systems with Unknown Actuator Backlash Compensation. Actuators, 2025, vol. 14, no. 6, art. no. 288. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060288.
Wang J., Xu W., Fang S., Chen Y., Wang Y., Wang W. Adaptive control schemes based on characteristic model for servo motor drives. IET Power Electronics, 2023, vol. 16, no. 13, pp. 2238-2248. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/pel2.12544.
Song C., Liu J., Yu J., Ma Y., Zhang X., Lv Z. Adaptive Fuzzy Finite-time Tracking Control for A Class of DC Motor with State Constraints. 2020 7th International Conference on Information, Cybernetics, and Computational Social Systems (ICCSS), 2020, pp. 682-686. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCSS52145.2020.9336834.
Xu C., Hu J. Adaptive robust control of a class of motor servo system with dead zone based on neural network and extended state observer. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2022, vol. 236, no. 9, pp. 1724-1737. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/09596518221099783.
Sai Lakshmi S., Jeyasenthil R., Babu U.B. Robust controller design based on IMC scheme for motion control of DC servo systems. In: Kumar S., Tripathy M., Jena P. (eds) Control Applications in Modern Power Systems (EPREC 2023). doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9054-2_16.
Yıldırım Ş., Bingol M.S., Savas S. Tuning PID controller parameters of the DC motor with PSO algorithm. International Review of Applied Sciences and Engineering, 2024, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 281-286. doi: https://doi.org/10.1556/1848.2023.00698.
Dong Z., Chen S., Sun Z., Tang B., Wang W. A Servo Control Algorithm Based on an Explicit Model Predictive Control and Extended State Observer with a Differential Compensator. Actuators, 2025, vol. 14, no. 6, art. no. 281. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/act14060281.
Cui P., Zheng Z., Fu J., Zhang Q., An L. A Fault-Tolerant Control Method for a PMSM Servo Drive System with a Four-Leg Inverter. Electronics, 2023, vol. 12, no. 18, art. no. 3857. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183857.
Amieur T., Taibi D., Kahla S., Bechouat M., Sedraoui M. Tilt-fractional order proportional integral derivative control for DC motor using particle swarm optimization. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 2, pp. 14-19. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.2.03.
Jastrzębski M., Kabziński J., Mosiołek P. Finite-Time, Robust, and Adaptive Motion Control with State Constraints: Controller Derivation and Real Plant Experiments. Energies, 2022, vol. 15, no. 3, art. no. 934. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en15030934.
Nguyen M.H., Ahn K.K. A Finite-Time Disturbance Observer for Tracking Control of Nonlinear Systems Subject to Model Uncertainties and Disturbances. Mathematics, 2024, vol. 12, no. 22, art. no. 3512. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223512.
Nguyen X.C., Le D.T. Adaptive finite-time synergetic control for flexible-joint robot manipulator with disturbance inputs. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2025, no. 3, pp. 45-52. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.3.07.
Khatir A., Bouchama Z., Benaggoune S., Zerroug N. Indirect adaptive fuzzy finite time synergetic control for power systems. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 1, pp. 57-62. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.1.08.
Chiem N.X., Thuy P.X. A Finite-time Controller Design Based on Strick-feedback System for Flexible Joint Manipulator. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2025, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 1829-1838. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-024-0939-4.
Vesović M., Jovanović R., Trišović N. Control of a DC motor using feedback linearization and gray wolf optimization algorithm. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2022, vol. 14, no. 3. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/16878132221085324.
Ambrosino, R., Ariola, M., Garone, E., Amato, F., & Tartaglione, G. New conditions for finite‐time stability of impulsive dynamical systems via piecewise quadratic functions. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2022, vol. 16, no. 13, pp. 1341-1351. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/cth2.12308.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Q. B. Nguyen, X. C. Nguyen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




