Association smooth-pole dual open-end windings permanent magnet synchronous machine with cascaded 2-level inverters for improved performances
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2026.1.08Keywords:
smooth-pole dual open end permanent magnet synchronous machine, cascaded 2-levels inverters, power segmentation, reliabilityAbstract
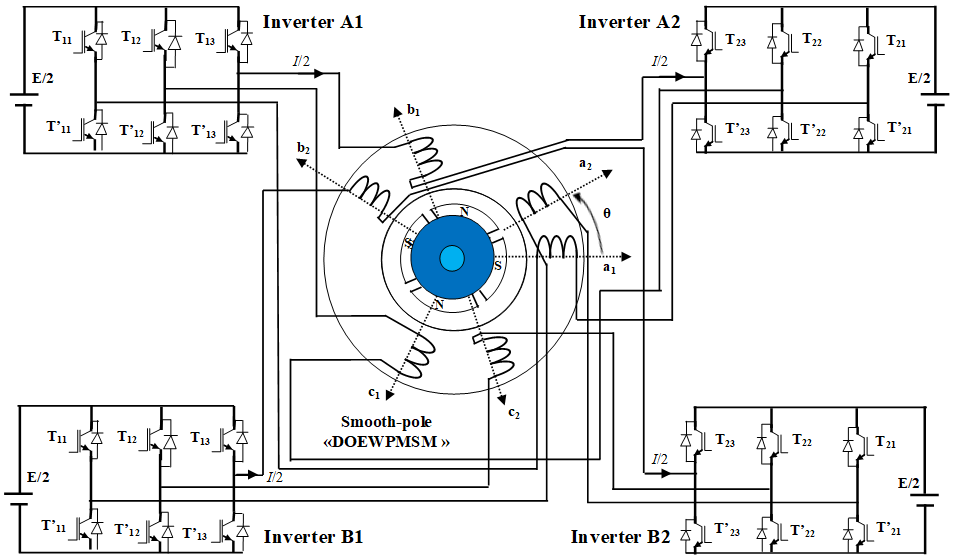
Introduction. Power segmentation is an increasingly important priority in high-power industrial drive applications that utilize AC machines. Problem. To improve the dynamic performance, reliability and power segmentation of drive systems in high-power applications (above the megawatt range), it’s advantageous to replace a single high-power converter with several low-power converters. This principle is applied to the combination of AC machines and inverter structures. Goal. The authors propose a novel dual open-end windings permanent magnet synchronous machine. This machine reduces the required size of the power supply inverters while also improving dynamic performances and lifespan. Its power supply using 2-levels cascading inverters, further enhances these performances. Methodology. For this study, the mathematical model of the system in the Park reference frame is introduced and validated using the MATLAB/Simulink environment. First, simulation results are presented for the proposed machine supplied by four conventional two-level inverters based on the pulse width modulation technique. Next, the new machine is fed by four multilevel converters, with each converter consisting of two two-level inverters. To further demonstrate the benefits of this converter structure, the authors then use a configuration with three cascaded two-level inverters. The results demonstrate that the use of the new machine with conventional two-level inverters ensures power segmentation and improves the quality of the voltage, stator current, and torque. Furthermore, associating this same machine with cascaded multilevel inverter structures significantly enhances dynamic performance and reliability. The scientific novelty lies in the synergy achieved by integrating the novel synchronous machine with the cascaded two-level inverters, enabling the system to simultaneously surpass conventional limitations in both performance and reliability. Practical value. A simulation model of the novel dual open-end winding permanent magnet synchronous machine was implemented to validate the superior performance achieved with cascaded multilevel inverter structures for voltage supply compared to conventional two-level inverters. References 19, table 2, figures 17.
References
Nemouchi B., Rezgui S.E., Benalla H., Nebti K. Fractional-based iterative learning-optimal model predictive control of speed induction motor regulation for electric vehicles application. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2024, no. 5, pp. 14-19. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2024.5.02.
Chaib Ras A., Bouzerara R., Bouzeria H. An adaptive controller for power quality control in high speed railway with electric locomotives with asynchronous traction motors. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2024, no. 2, pp. 23-30. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2024.2.04.
Oshurbekov S.K., Kazakbaev V.M., Prakht V.A., Dmitrievskii V.A., Paramonov A.S. Analysis of electricity consumption of induction motors of IE1 and IE2 efficiency classes in a 11 kW pump installation. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2020, no. 5, pp. 18-24. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2020.5.03.
Ebrahimi F., Wndarko N.A., Gunawan A.I. Wild horse optimization algorithm implementation in 7-level packed U-cell multilevel inverter to mitigate total harmonic distortion. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2024, no. 5, pp. 34-40. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2024.5.05.
Parimalasundar E., Muthukaruppasamy S., Dharmaprakash R., Suresh K. Performance investigations of five-level reduced switches count Η-bridge multilevel inverter. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 6, pp. 58-62. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.6.10.
Benboukous M., Bahri H., Talea M., Bour M., Abdouni K. Comparative analysis of principal modulation techniques for modular multilevel converter and a modified reduced switching frequency algorithm for nearest level pulse width modulation. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2025, no. 4, pp. 26-34. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.4.04.
Sujatha M.S., Sreelakshmi S., Parimalasundar E., Suresh K. Mitigation of harmonics for five level multilevel inverter with fuzzy logic controller. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 4, pp. 52-56. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.4.08.
Priyanka G., Surya Kumari J., Lenine D., Srinivasa Varma P., Sneha Madhuri S., Chandu V. MATLAB-Simulink environment based power quality improvement in photovoltaic system using multilevel inverter. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2023, no. 2, pp. 43-48. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2023.2.07.
De Gaetano D., Harikumaran J., Sala G., Degano M., Buticchi G., Gerada C. On Torque Improvement by Current Harmonic Injection in Isotropic and Anisotropic Multiphase Machines. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Industrial Electronics, 2022, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 845-853. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/JESTIE.2021.3105337.
Sun J., Zheng Z., Li C., Wang K., Li Y. Optimal Fault-Tolerant Control of Multiphase Drives Under Open-Phase/Open-Switch Faults Based on DC Current Injection. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 5928-5936. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2021.3135280.
Chaabane H., Khodja D.E., Chakroune S., Hadji D. Model reference adaptive backstepping control of double star induction machine with extended Kalman sensorless control. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2022, no. 4, pp. 3-11. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2022.4.01.
Darsouni Z., Rezgui S.E., Benalla H., Rebahi F., Boumendjel M.A.M. Ensuring service continuity in electric vehicles with vector control and linear quadratic regulator for dual star induction motors. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2025, no. 2, pp. 24-30. doi: https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272X.2025.2.04.
Chatterjee S., Kastha D. A New Multilevel Converter Configuration for Medium-Voltage Open-Winding PMSG-Based Wind Energy Conversion Systems. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Industrial Electronics, 2024, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 39-49. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/JESTIE.2023.3293428.
Yu Z., Chen Y., Zhao J., Zhang X., Zhou X. Alternate Subhexagonal Center Dual-Inverter PWM Scheme for Open-End Winding DC-Biased-VRM Drive Using Adjustable Zero Voltage Vector With Dead-Time Effect Compensation. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2025, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 7322-7333. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2025.3526609.
Jiang C., Liu H., Wheeler P., Wu F., Huo J. An Optimized Modulation for Five-Phase Open-End Winding PMSM With Sliding Clamped Strategy. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, vol. 70, no. 9, pp. 8819-8829. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2022.3212385.
Guizani S., Ben Ammar F. Dual open-end stator winding induction machine fed by redundant voltage source inverters. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences, 2015, vol. 23, pp. 2171-2181. doi: https://doi.org/10.3906/elk-1305-80.
Nayli A., Guizani S., Ben Ammar F. Modeling and analysis of a novel dual open-end stator windings wound rotor synchronous machine with dampers. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences, 2017, vol. 25, pp. 995-1009. doi: https://doi.org/10.3906/elk-1506-250.
Guizani S., Ben Ammar F. Torque and current enhancement based on dual open-end stator winding IM at 0 fed by two 2-level cascaded inverters. Electrical Engineering, 2018, vol. 100, no. 3, pp. 1869-1879. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-017-0668-2.
Guizani S., Nayli A., Ben Ammar F. A generalized mathematical model of the two-level cascaded inverters feeding the open-end stator winding induction machine. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2014, vol. 14, no. 4, 10 p.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 A. Nayli, S. Guizani, F. Ben Ammar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.




